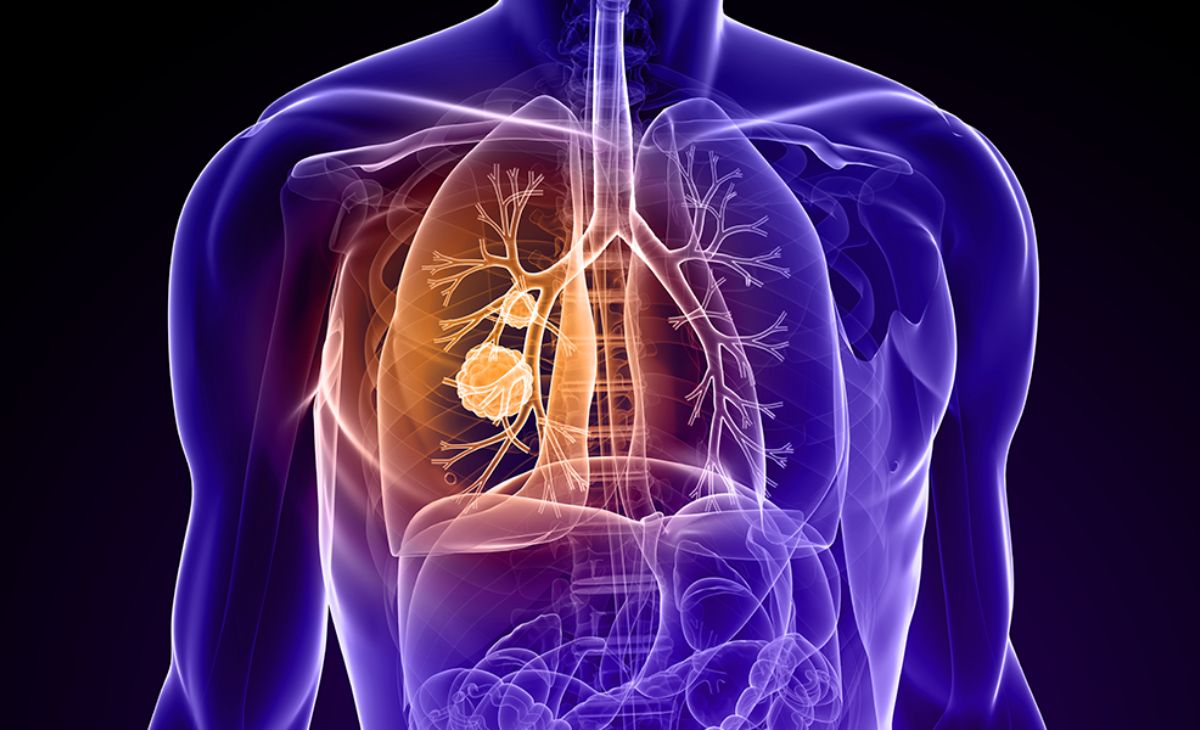
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, complicated by societal stigma, misconceptions, and late-stage diagnosis. Despite medical advances, the disease continues to challenge health systems. Key factors include the stigma associated with lung cancer, tobacco usage patterns, the need for early detection, and the benefits of HRCT screening. Dr. Sanjay Deshmukh highlights that misconceptions about the disease primarily affecting smokers overshadow the fact that nearly half of the cases occur in non-smokers, particularly in regions where tobacco is chewed. Effective management requires increased awareness, promotion of early screening, and support for nationwide screening programs.
5 Major Key Points
- Stigma and Misconceptions: A major barrier to effective lung cancer management is the stigma and misunderstanding that it mainly affects smokers, while nearly 50% of cases occur in non-smokers.
- Tobacco Usage Patterns: In countries like India, where tobacco is often chewed rather than smoked, the focus on smoking as the primary risk factor can delay diagnosis for those who do not fit the typical smoker profile.
- Role of Early Detection: Late diagnosis remains a challenge. Symptoms are often mistaken for less severe conditions, making early detection critical. HRCT of the thorax has proven effective in catching the disease early.
- Recommendations for Screening: Implementing a population-based screening program with low-dose HRCT thorax screenings is essential for high-risk groups to improve early detection and intervention.
- Action Steps: Increase public awareness about diverse risk factors, promote early screening with HRCT, and support nationwide screening initiatives to enhance early detection and survival rates.